Fast and friendly network scanner. About; Screenshots; Download; FAQ; Contribute; Features. Scans local networks as well as Internet; IP Range, Random or file in any format. It runs on Linux, Windows, and Mac OS X, possibly supporting other platforms as well. 26 Dec 2019 » Mac maintainer wanted; 29 May 2017 » GitHub. A MAC address scanner scans the network for IP addresses and their associated MAC addresses. It enables users to scan hosts one at a time or a group of hosts at a time. MAC scanners allow users to find the IP and MAC addresses of devices accessing their network and to trace crucial client information like DNS engagement and hostnames.
Scanning for IP address lets you have better control over your network. With 1-2 commands, you can quickly map out the devices in your network and the IP addresses that they are using. But to understand how to scan a network, first, you need to understand how are IP addresses assigned.
DHCP (Assigning IPs Dynamically)
An automated process in networking, called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), assigns IP dynamic addresses to hosts as soon as they enter the network. In a home or small network, the DHCP server is usually a part of the router. When you come into the network, the router will look for an available IP address in its pool and assign it to you, so that your device can communicate with others without any conflict.
Dynamic allocation of IP addresses is a great advantage for both end-users and network admins. But sometimes you would need to have some control in order to manage and troubleshoot your network more efficiently.

What will you learn in this Tutorial
In this tutorial, you will learn the basic networking skills on how to scan a network for IP addresses. We will scan a network with native OS commands, find which addresses were assigned dynamically, which statically, and test their connectivity.
In the end, we will compare some IP address scanning tools that can give you additional information. To improve your IP addressing insights, even more, we will show you some tools that allow you to track IP addresses and even manage them.
Simple IP Scanning
Operating Systems, like Windows and Linux, come with their own native simple networking set of tools. Commands such as “ipconfig”, “arp -a”, or “ping” allow simple scanning and troubleshooting.
The simplest way to get a quick list of IP addresses and their devices connected to your network is with those OS native commands found in the command line. With a list of the assigned IP address and their devices, you can easily find the devices that are causing the most problems.
- ipconfig
This command displays all network settings assigned to one or all adapters in the computer. You can find information such as your own IP, subnet, and Gateway. For Linux and MacOS is “Ifconfig”. - arp -a
When you issue the “arp -a”, you’ll get IP-address-to-mac conversion and the allocation type (whether dynamic or static) of all devices in your network. - Ping
It helps determine connectivity between two hosts and find the IP address of a hostname.
- ipconfig
Reading The Output
Finding your own network adapter configuration
In the following screenshot, you’ll see the output from the ipconfig command. On a Windows, the ipconfig command can be entered through the Command line.
Go to Run > type cmd > type ipconfig
- This Windows computer has 5 network adapters, but the last one (Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi) is the only one connected to a network. The rest are disconnected.
- In this network, the router (or Default Gateway) is playing the role of the DHCP server. It is assigning the IP address dynamically and giving access to the Internet.
- You are reading two of the most important IP addresses for your device; Your own device’s IP (IPv4 and IPv6) and your Gateway. The Subnet Mask is also very important, it shows that you are on the same subnet as the gateway.
Now you know your subnet, which in this case is 192.168.1.0/24 (using the CIDR range). Now you need to find the rest of the IP address in your network.
Scanning your Network
The job of the ARP protocol is to map IPs to MAC addresses. It provides a method for hosts on a LAN to communicate without knowing any address and create a cache of information. When a new computer enters the LAN, it receives an IP and updates its ARP cache with the Gateway information. This ARP cache can be found using the “arp-a” command.

- Use the command line to enter the “arp -a” command.
- This computer has been connected for some time into the LAN, so its ARP cache is very precise and complete. The first IP address shown in the display is the Gateway (the same we found through the ipconfig command).
- The output shows the IP, the MAC addresses, and their assignation type. The addresses displayed here were dynamically assigned by the DHCP server in the LAN. All of these IPs are devices connected to the LAN (192.168.1.0/24). The other static addresses are reserved for Multicasting.
- With the MAC information, you can know the vendor. Try searching for vendor prefixes or use an automatic online tool such as MACvendors.
Testing Connectivity
Finally, with some information, you can test connectivity. In the following test, we tried an extended ping with “ping -t” to the gateway. With this, you can learn some simple insights about delay and latency.
From the list generated by the ARP command, you could ping all the live hosts. Or you can go beyond and ping the entire subnet to find hosts not found by the ARP (but that would be too much manual work…). Later, we’ll discuss how to automatically ping entire subnets at once.
Although having a list of devices and their allocated IP address will give you good insights, the information will not be enough when your network scales. Manual IP scanning in multiple subnets and BYOD (Bring-Your-Own-Device) scenarios is nearly impossible. As the network scales, problems will scale too.
Larger networks demand more results, flexibility, and easy-to-read set of commands.
An IP Address Scanner tool helps you with larger demands. These tools are able to map the entire local network, finds live hosts, and to provide the results of the “arp-a” in a clearer format. Other IP Scanners do not depend on ARP but they operate using repeated ping tests. A Ping Sweep tool lets you ping entire subnets and find live hosts just with one button.
Some other IP Scanners go the extra mile and give more information such as Port number, DNS, DHCP, etc. All of this data is also presented in the most visual and easy-to-read format. They also allow users to save all results and present them in detailed reports.
Advanced IP Scanners
1. Angry IP Scanner
Angry IP Scanner is one of the most popular scanners on the web, with over 29 million downloads. It is open-source, free, and available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux. It can let you scan your local network or the Internet-facing IP addresses.
/ResetPrintSystem-56a5d49f5f9b58b7d0de9f1e.jpg)
This tool is not only capable of scanning IP addresses but also ports. When you define an IP address range, you can also specify a number of the port, and see if a device in your network is using a specific service (defined by the port). Angry IP Scanner also lets you save all the scan results into multiple formats, such as TXT, XML, CVS, etc.
When you scan, you’ll know what hosts are alive, their response time, hostname, MAC address, etc. If you want even more information, you can extend results by developing Java plugins.
Price:
Open Source and 100% free.
Download:
Get Angry IP from its official site.
2. SolarWinds Ping Sweep
Ping Sweep from SolarWinds helps you find free IPs and identify which ones are unavailable. It is classified as a networking discovery tool from the SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset. A comprehensive network software, that includes over 60 handy tools. Ping Sweep from SolarWinds is included in the Engineer’s Toolset and is dedicated for ping testing. For the MAC address, port scans, SNMP scans, etc, there are more dedicated tools in the Engineer’s Toolset.
Just as when you ping from the command line, this tool shows the DNS name for each IP and response time. It can also let you export results in different formats such as CSV, TXT, XLS, and to an HTML page.
Price:
SolarWinds Engineer’s Toolset starts at $1,380.00 and includes over 60 must-have tools.
Download:
Get a fully functional Engineer’s Toolset for 14 days by registering to SolarWinds official site.
IP Address Tracker Tools
Having a map of IP addresses, MAC addresses, used ports, etc, is great for networking inventorying and may help with some troubleshooting cases. But a list can not control and display real-time results.
An IP address Tracker is a good upgrade to our set of tools and commands described so far. It does allow scanning multiple subnets and displaying results, but it also allows you to keep track of one or more IP addresses.
An IP Address Tracker will notice when an IP address is released. This can be either because the device lost connectivity or it changed IP address. It will help you minimize IP addressing conflicts (when two devices are trying to take the same IP) and reduce DNS errors.
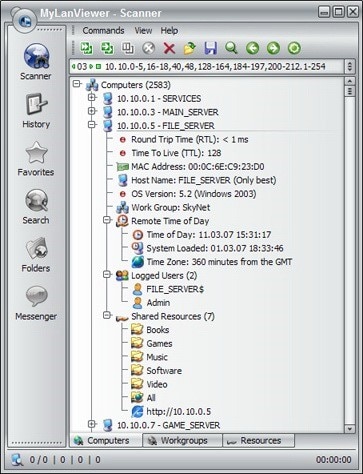
3. MyLAN Viewer
MyLAN Viewer is a NetBIOS and IP address scanner for Windows systems. Just like the IP Scanners shown above, this tool will scan a network and show devices in an easy-to-read format.
But MyLANViewer goes beyond, and not only shows computer name, IP, and MAC, but also NIC, OS version, logged users, shared folders, and much more.
This tool is able to track specific IP addresses and show notifications when their state change. With it, you can also keep track of network security by showing port information and detecting rogue DHCP servers. MyLAN Viewer tracks all devices in the subnet including hidden, and displays alerts when new devices enter the network, and others go.
This tool can also display the following metrics as well:
- Display Whois data.
- Perform traceroute.
- Manage “Remote Shutdown and Wake On LAN (WOL)”.
- Monitor wireless networks.
Price:
Free, but only available for Windows systems.
Download:
Get MyLAN Viewer from its official site.
4. SolarWinds IP Tracker
SolarWinds IP Tracker is a standalone software and completely free. In addition to creating inventories of all devices, this tool allows you to scan, track, and manage IP address, including their event logs, all in a single place. SolarWinds IP Tracker is the free version and feature-limited of the much coveted IP Address Manager.
But the IP Tracker does an amazing job to provide a centralized view of the entire IP addressing scheme. It lets you monitor 256 (one subnet) IP addresses for free. Additionally, this tool allows basic management functionalities with tools such as, Ping, Telnet, Traceroute. The best of all is that, with SolarWinds IP Tracker you can detect IP address conflicts created by misconfigured DHCP servers.
SolarWinds IP Tracker is only supported by Windows systems.
Price:
100% Free.
Angry Ip Scanner For Mac
Download:
Register in SolarWinds to download the software for free.
IP Address Management (IPAM)
Basic IP Address Scanning should be enough to manage small networks. But when networks scale they depend on multiple subnets and detailed management requirements. Although SolarWinds IP Tracker is able to find IP address conflicts, it is not able to control them.
Sometimes large-scale networks have standalone DHCP and DNS Servers in order to assign addresses to multiple subnets. But IP conflicts occur and it is really challenging to manage them manually. An IP Address Management or “IPAM” is a piece of software able to actively control DHCP and DNS. It also gives you the ability to manage multiple subnets.
5. SolarWinds IP Address Scanner
Among SolarWinds powerful tools, the IP Address Manager does everything a large-scale enterprise needs to manage its addresses properly. It automates many processes to make IP Address management easier. From automated IP address tracking, quick static IP reservations, to multi-vendor DHCP and DNS support.
SolarWinds IPAM comes with an integrated IP address management, DHCP, and DNS tools to administer your entire network.
One of the most commonly used tools from this bundle is the IP Address Scanner. This tool allows you to create automated IP address scans to maintain an updated inventory of all IP address blocks in the network. This is achieved by sending regular ICMP and SNMP polls. The automatic scans use ICMP polls to gather status of the IP address and hostname information. It also uses SNMP to find information on MAC addresses and other vendor information. SolarWinds IP Address Scanner supports both IPv4 and IPv6 address management.
SolarWinds IPAM also provides detailed reports of your IP address in real-time.
Price:
Download the Free Trial for 30 Days!
Download:
Get a fully functional SolarWinds IPAM for 30 days by registering to SolarWinds official site.
Without the right tools, network administration can be a nightmare. Every minute of uptime needs to be meticulously maintained through sheer will. Or does it? For years, network administrators have been using networks scanners to automate the process of scanning devices throughout corporate networks. The main incentive has been to improve transparency over the network.
A network scanner will help you document the network, monitor it, and guard it. Here are some systems administration tasks that network scanners can help with:
- Device auditing – get a list of all live equipment on your network. Recheck for missing devices that would indicate equipment failure.
- Network mapping – create a graphical representation of your network from your device inventory. Many network scanners will perform this task for you
- Security procedures – spot rogue devices on your network
- IP address management – scan for duplication of IP addresses
- DHCP reconciliation – check for expired DHCP leases and IP addresses that are no longer active that enable you to return discarded addresses to the allocation pool
- Subnetting – log IP address ranges that indicate your subnet and look out for range exhaustion
- Capacity planning – begin your resource planning with a list of active devices on the network
Network scanners are invaluable to network administrators because they eliminate the need to manually scan network devices via the command line. Scanning for devices automatically frees up time for the administrator to do other important tasks. Network scanners are also the only reliable way to troubleshoot your network and ensure its longevity on an ongoing basis.
Attempting to run scans manually through the command line will leave you unable to keep up with the demands of your network. A basic network can have hundreds of different networks and IP addresses to manage. Even the most attentive administrator will struggle to keep up to date in this environment. At the best of times this leads to inefficiency but at worst, it leads to damage. Advanced IP scanners can even automate many of your auditing tasks and provide deeper intelligence on your inventory than a standard operating system command could give you.
Initially, finding a comprehensive networking scanning tool can seem like a tall task. However, with a little bit of research it doesn’t need to be. We’ve put together a guide to help you find some of the most competitively priced tools on the market.
Here is our list of the best Network Scanners for Windows:
- SolarWinds Network Device Scanner(FREE TRIAL) Part of the Network Performance Monitor, this module identifies all connected devices by using SNMP procedures. Installs on Windows Server.
- ManageEngine OpUtils(FREE TRIAL) A network utility bundle that includes four scanners to discover connected devices. Installs on Windows Server and Linux.
- PRTG Network Monitor A network discovery sensor as part of a network and infrastructure monitoring suite. Installs on Windows Server.
- Advanced Port Scanner A free IP address and port scanner that also logs MAC addresses, hostname, and port protocols.
- GFI LanGuard A network management system that includes device discovery. Available for Windows, Mac OS, and Linux.
- PortScan and Stuff A free network scanner that can identify open ports on all network-connected devices.
- Nagios Discovery Tool A Nagios XI component that offers four scanning methodologies.
- MiTeC’s Network Scanner A multi-threaded scanner with four different operating methods.
- OpenNMS A free, open source network management tool with a scanner included.
- Xirrus Wifi Inspector A real-time network monitor for wireless systems that includes SSID scanning to identify nearby devices.
- Capsa Free Network Analyzer An attractive free network monitor that is based on Wireshark – a paid version is also available.
- Nmap A very popular free command line network scanner and device identifier.
- The Dude Suitable for SMEs, this network scanner automatically produces a range of network maps.
WhatsUp Gold A network monitoring system that includes a device discovery feature and network topology mapper.
1. SolarWinds Network Device Scanner(FREE TRIAL)
First up on our list, we have SolarWinds Network Device Scanner, which is one of the SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor tools. SolarWinds Network Device Scanner is a program that uses SNMP to identify and flag active devices on your network. One of best things about Network Device Scanner is its slick user interface. It is very easy to use and the visual displays make it very easy to see what is happening on your network in real time.
A number of features mark this tool out as an advanced IP scanner. All the user needs to do start using Network Device Scanner is enter a list of IP addresses and the program will start the auto-discovery process on your network devices. You can also schedule regular auto-discovery as well, which makes this a program with scalability in mind. When your devices are logged in SolarWinds, you can monitor their performance via the platform’s simple GUI dashboard. You can also display this data in charts or graphs to make it easier to use as well.
Overall SolarWinds Network Device Scanner is a great offering because it allows you to have transparency over a large network. SolarWinds Network Device Scanner is one of the SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor tools and is available for $3,043 (£2,245). There is also a 30-day free trial period available here.
2. ManageEngine OpUtils (FREE TRIAL)
ManageEngine OpUtils is an IP address manager (IPAM) and switch port mapper. Network scanning is an integral part of these two functions and the console of the system also makes a Network Scanner Tool available for on-demand system scans.
The network scanner can search through a range of IP addresses or a non-sequential list. The scan can be requested via a number of methods:
- Ping Scan
- SNMP Scan
- MAC Address Scan
- DNS Scan
Once active IP addresses are identified, the tool will list them in the lower panel of the screen, showing hostname and MAC address as well as the IP address in use.
The other functions in the OpUtils package also prove useful for anyone wanting to manage IP address allocation. For example, the IPAM will probably be the next screen you jump to.
OpUtils installs on Windows Server and Linux. ManageEngine makes the tool available for a 30-day free trial.
3. PRTG Network Monitor
Many network administrators are familiar with PRTG Network Monitor, which has made waves as a versatile network scanner in the past. If you want to monitor your network and maximize your uptime, you can’t go wrong with PRTG Network Monitor. PRTG Network Monitor tracks your network usage through a variety of methods including Netflow, SNMP, and WMI. It also has roughly 170 different sensors available for app, SLA, and virtual server monitoring.
Its extensive notification feature make it ideal for network administrators looking to take a less hands-on approach. Status and threshold alerts keep you updated when a network event happens and you need to take action. In the event that something does come up, you can use the diverse report feature to break it down even further.
PRTG offers both a free and a paid version. The paid version costs $1,429 (£1,055) for 1000 sensors or $9,532 (£7,037) for 5000 servers. Pricing options are available from the Paessler website and you can download a 30-day free trial.
4. Advanced Port Scanner
When it comes to inexpensive network scanners, Advanced Port Scanner for Windows is one of the most popular tools available to date. Advanced Port Scanner is available up until Windows 8.1 in 32-bit and 64-bit formats. This program allows you to scan hundreds of IP addresses simultaneously with fast multithreaded port scanning. This really speeds up the discovery process. It can also access the names and addresses of computers via their TCP ports, adding further visibility.
Advanced Port Scanner is a great tool if you want to scan IP’s on your network and gain network transparency without spending any money. The best part about Advanced Port Scanner is that it is free. If you’d like to download Advanced port scanner it can be downloaded here.
5. GFI LanGuard
If you’re looking for a lightweight network scanner that you can deploy quickly, GFI LanGuard is an excellent choice. With a fast track installation process that will see you up and running within minutes, LanGuard is ideal for companies that want a low maintenance network scanning solution.
LanGuard’s dashboard takes a back-to-basics approach with its Windows-inspired dashboard. GFI is available on Windows, Mac OS and Linux, making it a good choice for companies looking for cross-platform potential. Likewise, the platform has a number of visualization features to help access your network performance quality (such as the ‘computer vulnerability distribution’ chart shown above).
LanGuard has a wider range of vulnerability management functions than other tools like Advanced Port Scanner. For example, you can use it to run patch management to ensure your network doesn’t miss any patches. Features like this are incredibly useful if you’re looking for a network scanning and monitoring solution all in one bundle.
GFI Languard is available for $26 (£17) a year for 25-49 nodes but decreases to $10 (£6.67) a year for 250-2999 nodes. There are a variety of pricing options available but GFI LanGuard is cheaper per node for larger organizations The free trial of this program can be downloaded here.
6. PortScan and Stuff
Another trustworthy network scanner that holds its own against the premium applications on the market is PortScan and Stuff. It has all the core features you would expect from a mid-range network scanner, with the ability to scan existing devices on your network and highlight open ports. The only limitation is the lack of visualization, which makes it a little more difficult to gain a cohesive picture of your network.
That being said, the filtering process does help to better your perspective of the network. For example, typing 3389 will flag up all devices that have the Remote Desktop Protocol active. While features like this do go a long way towards improving the feel of PortScan, they aren’t enough to bridge the gap made by the lack of visual elements available. If you’re interested in using PortScan, it can be downloaded for free online here.
7. Nagios Discovery Tool (Nagios XI)
Nagios have been an established name in the network monitoring space for quite some time, and Nagios Discovery Tool has established itself as a dependable platform for network administrators. You can use the program to scan for discoverable hosts in multiple ways: Nmap, Ping, SNMP and TCP. In terms of dictating the criteria through which a scan will run, you can select an IP range.
The only drawback is that Nagios Discovery Tool is only available through Nagios XI. Nagios XI offers users a 60-day free trial. After the trial period finishes, you can buy Nagios XI for a price of $1,995 (£1,471). If you decide to purchase Nagios XI you will also have access to range of other network monitoring tools and data visualization. Nagios XI can be downloaded from the company website here.
8. MiTeC’s Network Scanner
One of the lesser known scanners on this list is MiTec’s Network Scanner. This multi-threaded scanner has the capacity to run a broad range of scans such as ICMP, IP, Port, SNMO and ActiveDirectory scans. MiTec’s diversity makes it useful for network adminstrators looking for versatile scanning functionality. The GUI doesn’t have a snazzy design, but it does the job rather well.
Once you’ve run a scan you can then save the results or print them. You can also export your data straight to CVS for further analysis. Like a number of the other tools on this list you can also access deeper information on your network elements and view information like: operating system, IP address, MAC address, domain, and general description.
The icing on the cake is that MiTeC network scanner is a free tool. You can download a copy of MiTeC Network Scanner from the MiTeC website here. One of the only drawbacks is that this platform doesn’t come with any form of user guide. While you can improvise and use your initiative you might find yourself scratching your head if trying to run more complex scans.
9. OpenNMS
In the world of network management, open source tools can be very hit or miss. OpenNMS is no exception. Through OpenNMS you can conduct comprehensive scans to view individual nodes and vulnerabilities. OpenNMS was primarily designed to help network administrators minimize downtime. For this purpose, it is extremely effective.
For an open source platform, OpenNMS looks rather presentable. The core dashboard provides you with a clear overview of your network and the tabs are listed within reach. OpenNMS’s biggest asset is its appearance, so if you’re looking for a well-designed network scanner, this is a tough choice to beat. But if you need more depth, then you might want to look elsewhere. OpenNMS is available for free and can downloaded from the company website here.
10. Xirrus Wifi Inspector
Network administrators who seek a more fresh-faced network scanner for Windows would be well advised to consider Xirrius Wifi Inspector. Xirius was designed to help troubleshoot network infrastructure and identify connected devices. With over 1 million downloads, this tool has certainly made a good impression on IT administrators around the world. As a real-time monitoring solution, Xirrus is very impressive.
Every network you detect shows information such as network SSID, network mode, signal strength, frequency, channel, and type of encryption. This information is invaluable for improving transparency. What really sets Xirrus apart from the competition is its contemporary dashboard. Having a graphically pleasing user interface makes it much easier to monitor your network. The onscreen charts provide you with an accurate snapshot of what is happening on your network in real time.
A free trial of Xirrus can be downloaded from the Riverbed website here, but you’ll need to contact the sales team in order to get a price for the paid version.
11. Capsa Free Network Analyzer
Capsa is Colasoft’s entry-level network analyzer tool. This is a product aimed at anybody seeking to monitor moderate network traffic and conduct regular network maintenance. In many ways, Capsa is a paid version of Wireshark. There are visible similarities between the two, but in many ways Capsa’s user interface considerably outperforms Wireshark’s.
If you’re ever in doubt of what changes are taking place on your network, you can simply click the graphs tab to view an extensive breakdown of the minutiae. Likewise the protocols tab will provide you with a display detailing all the different types of traffic active on your network. Its features like this that make Capsa one of the most user-friendly applications on this list.
Two license options are available for Colasoft’s Capsa. A single seat perpetual license costs $995 (£734) and a 5 Seat Perpetual License is available for $4,475 (£3304). Both versions can be downloaded from the Colasoft website here.
12. Nmap
When it comes to network scanning tools, almost every administrator has used or at least heard of Nmap. The reason is that this is one of the top free network scanning tools on the market. Nmap can be used to run port scans throughout your network, locate vulnerabilities, and troubleshoot your connection.
Nmap is far from a superficial network scanner. Once it discovers a computer, it can identify a range of information about the device such as: OS, device, active software, and version number. This information is useful because it helps to build up a more complete picture of your network.
One of the biggest advantages of Nmap is that it is such a well known tool that there are hundreds of online resources available to help you use it. This means that even new users can take the time to research how to use Nmap and maintain their IT infrastructure on an enterprise level. If you’re not a fan of command line interfaces, then you might want to move on to a device with a friendly GUI. As an open source platform, Nmap can be downloaded for free here.
13. The Dude
Then there is The Dude. This network monitor has developed a name for itself as a solid network scanner for SMEs. Its auto-discovery feature is great at automatically identifying devices even when compared to other paid tools. The best part is that the initial setup process is incredibly quick, so you don’t have to spend ages tweaking configurations before getting started.
The Dude also has the ability to provide the user with notifications. You can go to the Notification File and configure email notifications in response to network events and other such incidents that require action. The only issue with The Dude is that there isn’t much documentation to support you. Though the user interface is simple to use, it is unfortunate that there is more direct information out there. The Dude is a free platform and is available to download through the MikroTik website here.
14.WhatsUp Gold
You get an initial network discovery phase when you install WhatsUp Gold. This network monitoring system will scan your network and identify Layer 2 and Layer 3 network equipment and also servers. The details of each device are recorded, including its device type, manufacturer, and serial number.
The results of the network test are logged in an inventory. This record of all equipment on the network is the basis for a network map. The WhatsUp Gold software will plot this map for you automatically.

WhatsUp Gold uses a Ping sweep and the SNMP method to explore the network. These processes keep running while the WhatsUp Gold software is still in operation. This means that WhatsUp Gold will continue to search for devices on the network. It might seem that the repetition of the network discovery process is a waste of time. However, this service means that you can add, change, remove, or move devices anywhere on the network and those changes will automatically be written to the inventory and result in a redrawn network map.
The network scan queries each device in turn to discover which other devices it is connected to. This results in links reaching out to cloud servers and remote sites as well as HQ networks. So, WhatsUp Gold is a good tool for mapping WANs and not just LANs. If you employ virtualization on your site, you would benefit from the WhatsUp Gold Virtualization Monitoring Add-on. This will focus on mapping the relationships between your servers and VMs, showing the applications and network links that deliver your VM environment.
On all network maps devices are shown as a circular icon. Each icon shows the IP address, the MAC address, or the hostname of the node — you select which of these identifiers you want to see. The rim of the circle is color coded to tell you the status of the device. These colors are red, yellow, and green, for alert, warning, and normal conditions. Links between devices are also color coded to show whether they are operating normally or congested.
The WhatsUp Gold software installs on Windows environments and you can get a 30-day free trial of the network monitor to give it a test before you commit money to the deal.
Network Scanners: Fundamental Tools
If there is one thing to take home about network scanners, it’s that organizations running enterprise-grade networks can benefit tremendously through automating their network scanning. In many ways it is impossible to manage a large network effectively if you’re scanning devices manually. Rather than running your network through the command line, it makes sense to incorporate the use of a quality network scanner.
Network Scanners For Mac
If you’re running a large network then incorporating a network scanner into your toolkit is highly advisable. All of the tools we’ve outlined above will serve you well in staying productive and managing your network. However, our top pick would have to be SolarWinds Network Device Scanner, as it is both scalable and easy to use for SME’s and larger organizations alike.
Ultimately, trying to monitor your network manually is a dead end. The time wasted trying to manually run port scans could be better spent actively observing your network. If you’re looking for a tool that gives you a better perspective of your network and allows you to troubleshoot poor performance, then you should definitely considering integrating a network scanner into your network maintenance strategy.
Ip Scanner For Mac
What Does a Network Scanner do?
Essentially, a Network scanner is an IP scanner which scans the IP of devices throughout your network. Typically they are used on enterprise grade networks with hundreds or thousands of computers. The primary purpose of a network scanner is to automate the process of locating devices and sharing resources across a large network. This is achieved by scanning IP addresses and IP ranges together.
Ip Scanner Mac Os
Why Do I Need To Use a Network Scanner?
Os X Network Scanner
As mentioned above, network scanners are used to identify devices and computers throughout a network. The reason why administrators need to use network scanners is that checking up on IP addresses manually simply takes too much time. Opening up command prompt and ping testing IP’s directly is a very inefficient way of checking up on your network. It not only means your wasting time doing this when you could be doing something else, but it’s hardly a suitable way to keep up to date with an enterprise grade network.
Free Mac Scanner Software
A network scanner will automate the process of scanning your network for computers, and show you which devices are active. By seeing what computers are active throughout your network you’re better able to monitor usage and run troubleshooting. You’re also in a much better position to respond to security events when they occur because you have network transparency.